To view this video content, you must accept YouTube cookies.
These cookies make it possible to share or react directly on the social networks to which you are connected or to integrate content initially posted on these social networks. They also allow social networks to use your visits to our sites and applications for personalization and targeting advertising.
The global pandemic hugely impacted the transport sector. Companies in aviation, maritime, logistics and other areas had to contend with disrupted or completely demolished supply chains, increased costs, worker shortages and many other difficulties. Traditional business practices and processes were wrecked. It was a time when they had to make do and mend and muddle through as best they could.
But post-pandemic, there is an opportunity to take stock and re-think. Transport companies can use this moment to undertake both evolution and revolution: they don’t need to embrace the business cliché of one or the other. Private 5G can be the mechanism that empowers transport and logistics companies to drive innovative new use cases that build on and complement existing ones. There’s no reason to throw out things that work only to replace them with new and shiny ones.
What can private 5G enable for transport and logistics companies?
Before COVID hit, transport and logistics companies tended to operate from a perspective of seeking small efficiencies through technology, reducing operating costs here and there. But post-COVID, it’s more a case of looking to implement major changes to existing ways of working. Aviation, shipping, cargo companies and the like want to reduce costs wherever possible.
Private 5G presents the possibility to power new use cases as well as bring more agility and visibility to existing ones. It can also enable companies to anticipate potential disruptions better. These are the sorts of areas that are driving digital transformation in transport now. For example, maritime companies could be looking to reduce roll-on/roll-off shipping costs. Aviation companies could look to reduce the costs of luggage movement around airports to save money on having planes sit on runways just waiting.
One of the shifts that needs to happen in transportation is the move from “just” ports and airports to fully-enabled smart transport hubs and campuses. The old vision of an airport or a port as a complex place of numerous siloed tasks and individual companies can, with 5G as a technology enabler, be transformed into an integrated campus and operate in a much more efficient manner for companies and consumers, too.
What other use cases can private 5G enable?
There is scope for use cases across many disciplines in smart transport hubs. And private 5G networks can ensure that the needs of multiple users and different use cases are catered to by marrying 5G speed and low latency to localized processing power and AI capabilities.
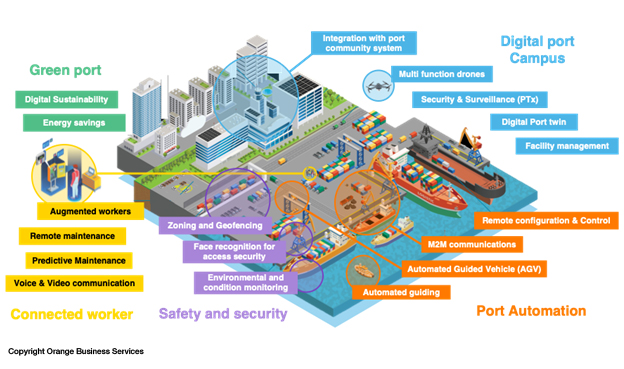
1. Unleashed connectivity capabilities
In maritime, smart ports can benefit from the aforementioned autonomous tugboats and connected cranes to make cargo lifting and shifting more efficient. Using existing connectivity, such as Wi-Fi, connected cranes struggle. 5G’s greater bandwidth, speed and reliability make them viable. 5G can enable drones at sites where sensitive cargo or security is a priority – the GSMA posits that 5G-enabled drones could be up to 15 times more efficient than fixed cameras . Autonomous forklifts and other cargo-moving vehicles can become commonplace. On the passenger side, it could become normal to see automated passenger buses ferrying travelers onto planes on the tarmac.
2. Better forecasting, smoother operations
Predictability and visibility can be improved using private 5G in evolved transport hubs: data analytics and AI enable more accurate forecasting, and increased visibility of passengers and cargo makes tracking more effective. Furthermore, enhanced levels of predictive maintenance and quality monitoring can also be enabled using sensors and computer vision.
3. Creating transport and logistics campus IoT hubs
In addition to vehicles shifting cargo and people around more efficiently, transport hubs are improved by static solutions and applications. Private 5G makes connected IoT systems more viable around a large site like a port or an airport, meaning connected traffic lights and parking management are enabled. Environmental monitoring sensors deployed around a site can ensure that visiting ships or planes are not exceeding emissions targets.
4. Next-level automated safety and security
Site security is improved by solutions like connected facial recognition, ensuring workers and site visitors can only access approved areas. IoT-powered asset tracking helps reduce loss and theft and ensures assets are where they are supposed to be. These are good examples of the evolution of existing transport hub applications, as is 5G enabling new communications around a port or airport site, transforming traditional tools like TETRA into push-to-X, video, and P2P group calls that leverage mobile connectivity.
Private 5G powering transport hub change
Orange Business has worked on two projects that are great case studies of this type of smart hub transformation. The Port of Antwerp and Port of Le Havre are examples where private 5G networks are driving change in existing applications and operations while enabling new ones.
At Antwerp, Orange has worked with the port to deliver a 5G standalone campus network. 5G’s faster speeds and lower latency have enabled new use cases like connected tugboats, computer vision and AI to help detect faults in high-voltage cables around the port. Software-defined networking (SDN) and network slicing mean tenant companies have their own bandwidth and latency tailored to their requirements. In Le Havre, 5G means tenant companies can benefit from real-time data transmission that enables connected robotics, AR maintenance solutions and autonomous vehicles. In both cases, the availability of 5G to enhance operations and reduce costs makes the port more attractive to potential new tenants.
Mission-critical communication: Digitalize and improve infrastructure
To view this video content, you must accept YouTube cookies.
These cookies make it possible to share or react directly on the social networks to which you are connected or to integrate content initially posted on these social networks. They also allow social networks to use your visits to our sites and applications for personalization and targeting advertising.
Augmented worker: Increase employee productivity
To view this video content, you must accept YouTube cookies.
These cookies make it possible to share or react directly on the social networks to which you are connected or to integrate content initially posted on these social networks. They also allow social networks to use your visits to our sites and applications for personalization and targeting advertising.
Computer vision to drive automation: Use robotics and automated guided vehicles (AVG) to drive automation
To view this video content, you must accept YouTube cookies.
These cookies make it possible to share or react directly on the social networks to which you are connected or to integrate content initially posted on these social networks. They also allow social networks to use your visits to our sites and applications for personalization and targeting advertising.
Enabling and complementing next-level transport hubs
It’s important to remember that 5G is an enabler of end-to-end use cases, it can connect transport hubs from devices through the infrastructure and then to the edge and to AI, but it is that: an enabler. It is not a replacement for existing wired and wireless connectivity around a port or airport; it is an adjunct to them. According to Gartner, 5G is also not the be-and-end-all. It is part of “wireless value realization”, whereby next-generation wireless technologies complement existing ones to “deliver new and improved services and reduced costs.”
Orange consultants understand this paradigm, how it works in the real world, and how to help customers translate the promise of private 5G into specific business contexts. It’s about understanding the opportunities that can be built on private 5G based on your challenges and drivers, how technically feasible they are for transport companies to do, and then implementing them within the value chain. From ports to airports to any other smart transport hub, 5G promises all kinds of potential.
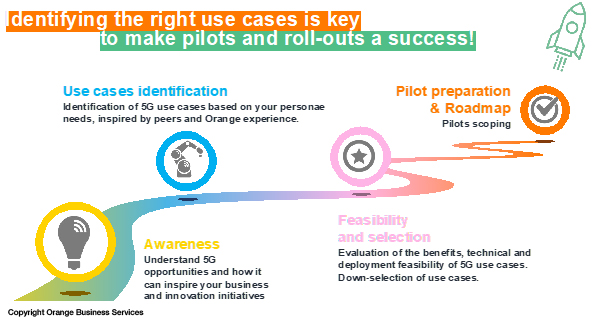
For more information, please feel welcome to reach out to our Business Consulting Team via our website or my email.
Read more about how Orange Business is helping businesses in the maritime and aviation industries and many more besides use 5G for evolution and revolution.

Antoine is a Consulting Lead for Europe. Antoine has over 13 years of experience in ICT business development, technical consulting, and business advisory at Orange in Singapore, the UK, and Switzerland. On weekends you can find him hiking, climbing, diving, or playing the piano.